Combat sudden tooth pain: uncover causes & solutions
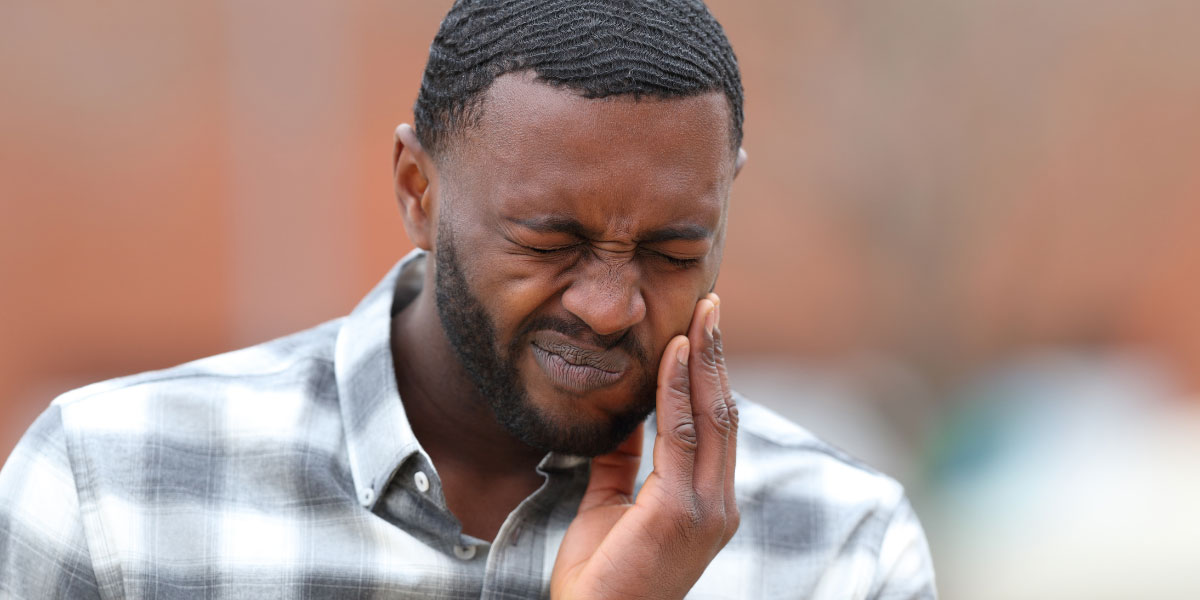

Sudden tooth pain requires a visit to your dental provider to determine & treat the cause. Learn possible causes, prevention and treatment essentials from a dental hygienist.
Tooth pain is often hard for one to ignore regardless if it is sharp, sudden, dull, or a constant ache.[1] The most common causes of tooth pain is an active tooth infection, decay, injury, or tooth loss.[1] At times pain might originate from other areas such as the jaw joint, ears, sinuses, and even from heart problems that radiate to your teeth and present as tooth pain.[1] Most causes of tooth pain are treatable by your dentist.[3]
What causes tooth sensitivity?
A toothache occurs when the pulp (central portion of the tooth) becomes sensitive to pain, often due to inflammation.[1] Common causes of pulpal inflammation are dental cavities, trauma, teeth grinding, gum disease, or infection.[1]
You might be experiencing pain due to having a cracked tooth. This can occur due to clenching or grinding your teeth or even chewing on hard foods such as ice, nuts, or hard candy[2]Some other causes of a cracked tooth are pressure from clenching or grinding your teeth, large fillings that weaken the tooth’s integrity, or trauma to the mouth.[2]
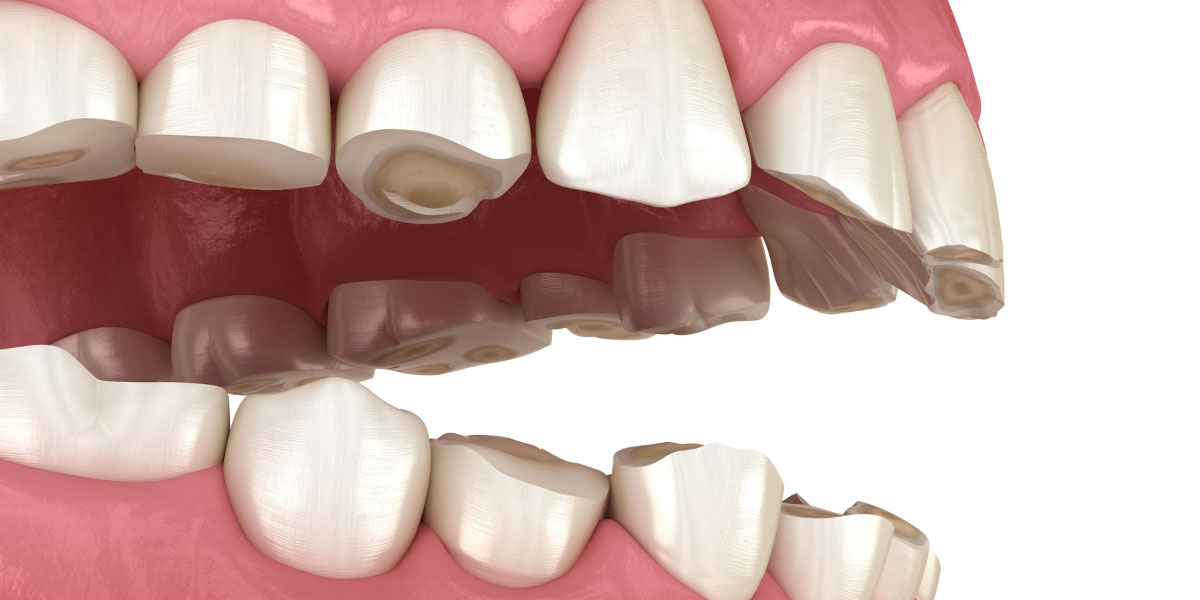
Complications of a cracked tooth
You should not ignore pain in your teeth as doing so could lead to complications. Infection from your tooth can spread to the bone, gums, and enter into your bloodstream. Your dentist will determine what treatment may be needed to treat your toothache by finding out what is causing the discomfort. Antibiotics will be prescribed if there is an infection present around the tooth, you have a fever, or swelling of the jaw is present[1]
Symptoms of a dental infection or a cracked tooth are a fever, pain when chewing, swollen gums, sensitivity to hot and cold food or beverages, and sore lymph nodes[2]
How tooth pain is treated
The dentist may recommend possible procedures such as fillings, extractions, root canal therapy, occlusal guard, or crowns.
- Fillings – A plastic resin restoration that is placed that resembles the natural look of the tooth is used to fill the crack and restore the tooth to its functionality.[2]
- Extraction- When the tooth is extremely decayed, cracked, or damaged then it will need to be extracted or permanently removed[2]
- Root Canal Therapy- when decay or a crack extends into the pulp a root canal is need to remove the damaged pulp and restore the integrity of the tooth, preventing further damage or infection.[2]
- Occlusal Guard – prevents damage to your teeth that can be caused by grinding and clenching
- Crown – a dental crown is usually made of porcelain or ceramic and fits over the tooth.[2]
Sometimes the dentist might recommend not to proceed with any treatment. If a patient has a hairline crack in the enamel of their teeth that doesn’t produce pain or negatively affect their appearance no treatment might be needed.[2]
How to prevent a toothache
Avoid chewing hard foods and use a mouth guard if you clench or grind your teeth. If you play contact sports wear a sports mouthguard to protect your teeth from injury.[2] Visiting your dentist regularly for preventative care can help your healthcare professional to address concerns when they are small and manageable[2] Receiving prompt treatment can help you reduce the risks of losing your tooth, further damage, and preventing harmful infection from spreading.[2] Brushing twice a day and flossing daily will help to prevent dental diseases that contribute to tooth problems.
- Web MD. https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/toothache
- Cracked Tooth. Christiano, Donna. (2018, September 28). https://www.healthline.com/health/cracked-tooth
- All My Teeth Hurt Suddenly: 10 Possible Explanations Watson, Kathryn. (2019, May 23). https://www.healthline.com/health/all-my-teeth-hurt-suddenly#cracked-tooth-or-crown